Ceo Vs. Co-Founder: Key Differences Explained
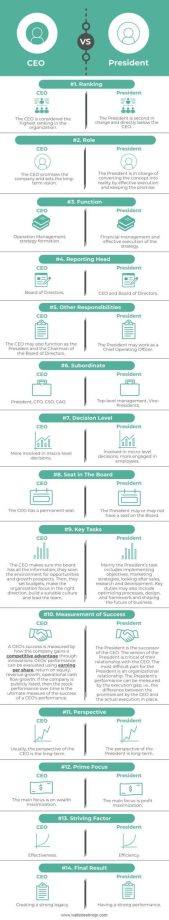
Starting a business requires a strong team, and two key roles in any organization are the CEO and the Co-Founder. While both positions hold significant responsibility, they have distinct differences in their roles, responsibilities, and relationships with the company. In this article, we will explore the key differences between a CEO and a Co-Founder, and the impact they have on the success of a business.
1. Definition and Roles
A CEO, or Chief Executive Officer, is the highest-ranking executive in a company. They are responsible for making major corporate decisions, managing the overall operations, and ensuring the company’s goals and objectives are met. The CEO is typically appointed by the board of directors or shareholders.
On the other hand, a Co-Founder is one of the initial members who starts a company along with one or more individuals. They are involved in the early stages of the business, contributing to the idea, product development, and securing funding. Co-Founders are usually actively involved in the day-to-day operations of the company.
2. Decision-Making Authority
A CEO has the final decision-making authority in the company. They are responsible for setting strategic goals, making business decisions, and ensuring the company’s profitability. The CEO consults with other executives and stakeholders but ultimately has the final say in important matters.
Co-Founders, on the other hand, have a significant say in decision-making, especially in the early stages of the company. They work closely with the CEO and other executives to make critical decisions that shape the direction of the business. However, as the company grows, the CEO’s decision-making authority may become more prominent.
3. Leadership and Management
A CEO is responsible for providing leadership and managing the entire organization. They set the company’s vision, mission, and values, and ensure that all employees are aligned with these objectives. The CEO also oversees the performance of other executives and managers and ensures effective communication throughout the organization.
While Co-Founders may also provide leadership, their role is more focused on the specific areas they are responsible for. They may lead teams or departments within the company, but their leadership role is often shared with the CEO and other executives.
4. Ownership and Equity
A CEO may or may not have ownership or equity in the company. They are typically hired by the board of directors or shareholders and are compensated through salary, bonuses, and other incentives. However, in some cases, a CEO may also be a significant shareholder or have equity in the company.
Co-Founders, on the other hand, are usually the owners of the company. They have a significant stake in the business and may have invested their own capital or intellectual property to start the company. Co-Founders are often motivated by the long-term success and growth of the company.
5. Relationship with Investors and Stakeholders
A CEO is responsible for building and maintaining relationships with investors, stakeholders, and the board of directors. They communicate the company’s financial performance, strategic plans, and growth opportunities to investors and seek funding or support for the company’s initiatives.
Co-Founders also play a role in building relationships with investors, especially in the early stages of the company. They may be involved in pitching the business idea, securing funding, and maintaining relationships with key stakeholders. However, as the company grows, the CEO often takes on a more prominent role in investor relations.
6. Hiring and Team Building
A CEO is responsible for hiring and building a strong team to support the company’s goals and objectives. They oversee the recruitment process, set hiring criteria, and make final hiring decisions. The CEO also plays a crucial role in developing and nurturing the company’s culture.
Co-Founders are often involved in the hiring process, especially in the early stages. They may help identify talented individuals, conduct interviews, and make recommendations. However, as the company grows, the CEO typically takes on a more centralized role in hiring and team building.
7. Succession Planning
A CEO is responsible for succession planning, ensuring that the company has a strong leadership pipeline for the future. They identify and develop potential successors, mentor key executives, and plan for a smooth transition in case of their departure.
Co-Founders may also be involved in succession planning, especially if they have a long-term vision for the company. They may groom other executives or future leaders within the organization. However, the CEO is primarily responsible for succession planning.
8. Accountability and Performance
A CEO is accountable for the overall performance and success of the company. They are responsible for achieving financial targets, meeting key performance indicators, and ensuring the company’s growth and profitability.
Co-Founders also have a level of accountability, especially if they hold executive positions within the company. They are responsible for the performance of their respective areas and contribute to the overall success of the business. However, the CEO has ultimate accountability for the company’s performance.
9. Relationship with the Board of Directors
A CEO works closely with the board of directors, seeking their guidance and approval on major decisions. They provide regular updates on the company’s performance, seek input on strategic initiatives, and ensure compliance with corporate governance.
Co-Founders may also have a relationship with the board of directors, especially if they are significant shareholders or hold key positions in the company. They may provide updates on their respective areas and seek support for their initiatives. However, the CEO takes the lead in board relations.
10. Long-Term Vision
A CEO is responsible for setting and executing the company’s long-term vision. They develop strategic plans, identify growth opportunities, and make investments to ensure the company’s long-term sustainability and success.
Co-Founders often contribute to the long-term vision, especially in the early stages of the company. They may have a specific vision or mission that they want to achieve and work with the CEO to align it with the overall goals of the business. However, the CEO has the primary responsibility for the company’s long-term vision.
Conclusion
The roles of a CEO and a Co-Founder are distinct yet interconnected. While a CEO provides overall leadership and management of the company, a Co-Founder plays a crucial role in the early stages and contributes to the company’s success. Both positions have unique responsibilities and relationships with the company, and understanding these differences is essential for the effective functioning and growth of a business.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the main difference between a CEO and a Co-Founder?
- Can a Co-Founder become a CEO?
- Do all companies have a Co-Founder?
- Is it better to be a CEO or a Co-Founder?
- Can a CEO be a Co-Founder?
The main difference between a CEO and a Co-Founder is their roles and responsibilities within the company. A CEO is responsible for the overall management and decision-making, while a Co-Founder is involved in the initial stages of the business and contributes to the idea, product development, and securing funding.
Yes, a Co-Founder can become a CEO if they have the necessary skills, experience, and qualifications to lead the company. In some cases, Co-Founders may start as the CEO and continue in that role as the company grows.
No, not all companies have a Co-Founder. Some companies may be started by a single individual, while others may have multiple Co-Founders. The presence of a Co-Founder depends on the specific circumstances and the vision of the individuals involved.
There is no definitive answer to this question as it depends on individual preferences and goals. Being a CEO allows for overall control and decision-making authority, while being a Co-Founder offers the opportunity to shape the company’s direction from the early stages.
Yes, a CEO can also be a Co-Founder if they were involved in the initial stages of the business and contributed to its establishment. In such cases, the CEO holds the dual role of being a founder and the highest-ranking executive in the company.
