Comparative Advantage: Benefits And Key Comparisons
Have you ever wondered why some countries specialize in producing certain goods or services while others focus on different industries? It all comes down to the concept of comparative advantage. In this article, we will explore the benefits of comparative advantage and delve into key comparisons that help us understand why countries engage in trade.
What is Comparative Advantage?
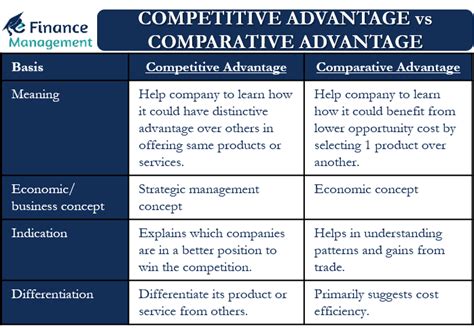
Comparative advantage refers to the ability of a country, individual, or organization to produce a particular good or service at a lower opportunity cost compared to others. It is based on the concept of specialization, where each entity focuses on producing what they are relatively more efficient at, and then trading with others to obtain a wider variety of goods and services.
Benefits of Comparative Advantage
1. Increased Efficiency
One of the main benefits of comparative advantage is increased efficiency in production. By focusing on producing goods or services that they have a comparative advantage in, countries can optimize their resources and achieve higher levels of productivity. This leads to improved economic growth and overall welfare.
2. Expanded Market Access
Through comparative advantage and international trade, countries can access larger markets for their products. When countries specialize in the production of certain goods or services, they can export these products to other countries and import the goods and services they need but may not be able to produce efficiently. This allows for a wider range of products to be available to consumers globally.
3. Enhanced Economic Cooperation
Comparative advantage fosters economic cooperation between countries. By engaging in trade, countries develop interdependencies and establish mutually beneficial relationships. This leads to increased diplomatic ties, improved political relations, and a more interconnected global community.
4. Resource Allocation
Comparative advantage helps in efficient resource allocation. Countries can allocate their limited resources to industries where they have a comparative advantage, ensuring optimal utilization and reducing wastage. This leads to a more sustainable use of resources and supports long-term economic development.
5. Technological Advancements
When countries specialize in certain industries, they tend to invest more in research and development, leading to technological advancements. This not only benefits the specialized industries but also spills over to other sectors, driving overall innovation and economic growth.
Key Comparisons in Comparative Advantage
1. Absolute Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage
While absolute advantage focuses on the ability to produce a good or service more efficiently than others, comparative advantage takes into account the opportunity cost of producing that good or service. Comparative advantage emphasizes specialization based on relative efficiencies rather than absolute efficiencies.
2. Ricardian Model vs. Heckscher-Ohlin Model
The Ricardian model of comparative advantage suggests that differences in labor productivity determine trade patterns, while the Heckscher-Ohlin model argues that differences in factor endowments, such as land, labor, and capital, drive trade. Both models provide insights into the factors influencing comparative advantage in different contexts.
3. Intra-industry Trade vs. Inter-industry Trade
Intra-industry trade refers to the exchange of similar goods or services within the same industry, while inter-industry trade involves the exchange of different goods or services between distinct industries. Both types of trade can be driven by comparative advantage, with countries specializing in different aspects of the same industry or focusing on completely different industries.
Conclusion
Comparative advantage is a fundamental concept in international trade that allows countries, individuals, and organizations to specialize in the production of goods and services they are relatively more efficient at. By engaging in trade based on comparative advantage, countries can benefit from increased efficiency, expanded market access, enhanced economic cooperation, optimal resource allocation, and technological advancements. Understanding key comparisons in comparative advantage, such as absolute advantage vs. comparative advantage, the Ricardian model vs. the Heckscher-Ohlin model, and intra-industry trade vs. inter-industry trade, helps us grasp the nuances of this concept and its implications for global economic dynamics.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between absolute advantage and comparative advantage?
Absolute advantage focuses on producing a good or service more efficiently than others, while comparative advantage considers the opportunity cost of producing that good or service.
2. How does comparative advantage lead to increased efficiency?
Comparative advantage allows countries to specialize in industries where they are relatively more efficient, leading to optimized resource allocation and higher levels of productivity.
3. What are the main models used to analyze comparative advantage?
The main models used to analyze comparative advantage are the Ricardian model and the Heckscher-Ohlin model, which provide insights into the factors influencing trade patterns.
4. Can comparative advantage lead to technological advancements?
Yes, comparative advantage can lead to technological advancements as countries specialize in certain industries and invest more in research and development.
5. How does comparative advantage foster economic cooperation?
Comparative advantage fosters economic cooperation by creating interdependencies between countries through trade, leading to improved diplomatic relations and a more interconnected global community.


